How does a general purpose electromagnetic relay work?
Have you ever wondered how a small electrical signal can control a much larger device without direct contact? The answer often lies in the general purpose electromagnetic relay, a key part of the General Purpose Relay family. This device is widely used in numerous electrical systems, playing a crucial role in managing the flow of electricity. Let’s explore how it works.
What is a General Purpose Relay?
A General Purpose Relay is an electrically - operated switch. It controls one electrical circuit by opening or closing contacts in another circuit. It enables a small control signal to switch on or off a larger electrical load, like motors or lamps. There are different types, including electromagnetic, solid - state, and reed relays. Among them, the general purpose electromagnetic relay stands out for its reliability, affordability, and ease of use.
Components of a General Purpose Electromagnetic Relay
A typical general purpose electromagnetic relay is made up of several key components:
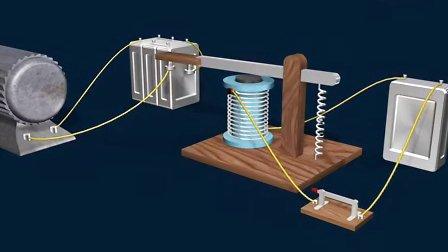
1、Coil: The coil, wound with insulated wire around a ferromagnetic core, generates a magnetic field when an electric current passes through it. The field strength depends on the coil turns, current magnitude, and core material.
2、Armature: This movable part, made of ferromagnetic material, is attracted to the coil when the magnetic field is present. It’s connected to the relay contacts and moves to open or close them.
3、Contacts: These are the switching elements, usually made of conductive materials like silver - or gold - plated copper. There are normally open (NO) and normally closed (NC) contacts. NO contacts close when the relay is activated, while NC contacts open.
4、Spring: The spring provides the force to return the armature to its original position when the coil’s magnetic field disappears, ensuring the contacts return to their normal state.
5、Housing: It encloses and protects the internal components from dust, moisture, and damage, and also serves as a mounting structure.
How Does a General Purpose Electromagnetic Relay Work?
The operation of a general purpose electromagnetic relay is based on electromagnetism. When current flows through the coil, it creates a magnetic field that attracts the armature. As the armature moves, it overcomes the spring force and changes the state of the contacts. If they are NO contacts, they close, allowing current to flow in the connected circuit; if NC, they open, interrupting the current.
When the current through the coil stops, the magnetic field collapses. The spring then pulls the armature back, and the contacts return to their original state. For example, in a circuit controlling a light bulb with a relay, closing a switch in the control circuit energizes the coil, closes the contacts, and lights up the bulb. Opening the switch turns off the bulb.
Advantages of General Purpose Electromagnetic Relays
General purpose electromagnetic relays offer several benefits:
1、Isolation: They provide electrical isolation between the control and load circuits, protecting the control components from high - voltage or high - current loads.
2、High Switching Capacity: These relays can handle large currents and voltages, suitable for powerful devices.
3、Simple and Reliable: With a straightforward mechanical design, they are easy to install and maintain and have a long service life when used properly.
4、Versatility: They can be applied in various scenarios, from basic on - off control to complex circuits, and work with both AC and DC.
5、Cost - Effective: Compared to some relays, they are relatively inexpensive.
Applications of General Purpose Electromagnetic Relays
General purpose electromagnetic relays are used in many industries:
• Automotive: To control systems like the starter motor, headlights, and air conditioning in cars.
• Home Appliances: In devices such as refrigerators, washing machines, and microwave ovens to manage motors and heaters.
• Industrial Automation: In PLCs and control systems for machinery, conveyor belts, and valves.
• Power Distribution: To protect circuits from faults by automatically disconnecting the power.
• Telecommunications: For signal switching, routing, and protection in communication equipment.
In conclusion, the general purpose electromagnetic relay is an essential device in modern electrical systems. Understanding its working principle helps us appreciate its wide - ranging applications and importance in ensuring safe and efficient operation of electrical equipment.
 中文
中文 Русский
Русский Español
Español


